Polkadot is a multi-chain framework platform — similar to Cosmos — designed to facilitate interoperability and scalability of blockchains that can plug into its ‘Relay Chain.’ Polkadot is an ambitious project that leverages a form of proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus for the broader ecosystem of blockchains that are connected to it.
Importantly, Polkadot allows data structures — outside of solely blockchains — to connect to the network as ‘parachains.’ Originally conceived by Gavin Wood — creator of the Solidity programming language –, Polkadot is a heterogenous multi-chain framework where parachains operate through a trust-minimized federation structure.
The scalability problems of blockchain networks are well-documented, and platforms like Polkadot are striving to become the next generation of networks that foster enhanced scalability and interoperability through expanding the design concepts of public blockchains and standardizing the transfer of data.
Read on as we cover this platform in more detail and also how and where to buy the Polkadot token DOT.
Where to Polkadot DOT
This section is our top picks of where and how to buy the Polkadot DOT Crypto token. We chose these based on our experience of using them and considered fees, security, payment options and reputation.
- Binance: Largest Crypto Exchange with Low Fees
- eToro: Easy to Use Platform
- Coinbase: Highly Regarded and Easy to Use for Beginners
Visit The Top Pick
eToro USA LLC; Investments are subject to market risk, including the possible loss of principal.
 Binance: Reputable Exchange with High Liquidity
Binance: Reputable Exchange with High Liquidity
Binance is the largest cryptocurrency trading exchange in daily trade volumes. The exchange offers investors full access to trade over 600 crypto assets.
The renowned platform also features a well-detailed learning curve and advanced trading tools that support well-experienced traders and investors looking to learn how to buy different cryptos. Although Binance features a user-friendly interface that facilitates a great user experience, it is more suited for well-experienced traders.
Read: Our Full Binance Review Here
Binance has a minimum deposit of $10. This enables investors to kickstart their investing journey with low fees. Investors can also initiate deposits through seamless payment methods like wire transfers, credit/debit cards, peer-to-peer (P2P) payments, and other e-wallet solutions.
Binance deposits come with a fee that varies based on the payment method used. For instance, the global exchange charges a standard fee of up to 4.50% for all deposits made with a debit/credit card.
All investors enjoy very low fees when trading on Binance, as it charges a standard trading fee of 0.1%. For investors that buy using Binance token (BNB), a discount of 25% on trading fees will be applied.
In addition, investors can rest assured that their funds and data are well protected whenever they trade on Binance. The broker features top-notch security measures like two-factor authentication (2FA), cold storage to keep most coins, whitelisting, and advanced data encryption to protect funds and data. Binance functions effectively in over 100 countries and has a spin-off regulated platform (Binance.US) that tends to US-based traders and investors.
Pros
- Trading fees at 0.01%
- High liquidity
- Wide range of payment methods
- 600+ crypto assets in library
Cons
- Interface is suited for advanced traders
- US-based customers cannot trade most coins via its subsidiary
 eToro: Easy to Use Platform
eToro: Easy to Use Platform
eToro is the one of the best exchanges to purchase crypto coins & tokens. It is one of the most popular social trading platforms in the investment space. This exchange gives traders and investors full access to trade over 78 crypto assets, including Bitcoin, Ethereum, and many more.
The broker’s user-friendly interface and simple layout is appealing to investors with no prior knowledge of crypto trading. To begin a trading journey on eToro, investors have to create an account. With a minimum deposit of as little as $10, US and UK-based investors can purchase tokens and other crypto assets seamlessly.
Investors also enjoy zero fees on all USD deposits, including debit card deposits. However, there is a standard fee charge of $5 on all withdrawals, a 1% flat fee for every completed trade on the platform, and a $10 inactivity fee charged monthly after an investor fails to trade for a year.
The broker offers seamless deposit methods that range from bank transfer and direct crypto deposits to debit/credit card and payment processors like PayPal. Although all USD deposits are fee-free, all bank transfer deposits have a fixed minimum of $500.
Another major feature that makes eToro stand out is its impressive CopyTrader feature. This integration enables novice investors to find well-experienced traders on the platform and copy their trade strategies to earn when they earn.
In terms of security, eToro scales to the top as it features two-factor authentication (2FA) protocol, advanced encryption, and masking technologies to secure all users accounts. eToro accepts users in over 140 countries and is regulated by top financial authorities like the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), Financial Conduct Authority (FCA), Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC), and the Cyprus Securities and Exchange Commission (CYSEC). The exchange is also registered with the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA).
Pros
- Overall best social trading platform to buy
- User-friendly interface
- CopyTrader and CopyPortfolio
- Highly regulated broker
Cons
- Charges an inactivity fee
- Charges a withdrawal fee
eToro USA LLC; Investments are subject to market risk, including the possible loss of principal.
 Coinbase: Simple & Easy to Use Exchange
Coinbase: Simple & Easy to Use Exchange
Coinbase is also a great option for investors looking for how to buy the crypto seamlessly. The US-based crypto trading platform enables users to buy, sell, and stake cryptocurrencies with zero complexity.
Coinbase integrates a user-friendly interface that simplifies crypto trading. The crypto trading platform supports well over 10,000 blockchain-based assets.
Read: Our Full Coinbase Review Here
The exchange’s signup and verification process take less than 10 minutes. For traders looking to invest easily, Coinbase is a great alternative to Binance.
Coinbase has a minimum deposit of $2, the lowest minimum deposit in the market presently This exchange also offers a wide range of deposit methods like automated clearing house (ACH), Wire transfer, debit card, and e-wallet solutions, as well as cashouts in local currencies like USD, GBP, and EUR. Coinbase charges up to 3.99% for debit card deposits.
Investors enjoy a 4% cash back reward whenever a Coinbase debit card is used for crypto purchases.
For fees, Coinbase charges a competitive fee of 0.5% - 4.5% depending on the payment method, cryptocurrency type, and transaction sizes.
Coinbase has evolved from a traditional exchange to a versatile platform with great services dedicated to retail and institutional investors, such as an in-built exchange wallet, self-issued cash back visa card, staking, derivatives, asset hubs, ventures, and many more.
Furthermore, Coinbase has in-built security practices like 2FA verification as an added security layer to investors’ usernames and passwords, crime insurance that secures digital assets from theft and fraud, and many more.
Also, Coinbase is licensed by the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and regulated by top financial authorities like Financial Conduct Authority (FCA), Financial Crimes and Enforcement Network (FinCEN), and the New York State Department of Financial Services (NYSDFS).
Pros
- Beginner-focused
- Licensed and reputable platform
- Insurance in case of hacks
- Low minimum deposit
Cons
- High fee compared to competitors
- No credit card deposits for US customers
The Polkadot Design
Polkadot explicitly identifies three primary areas that current blockchains struggle with to realize their full potential for providing practical applications:
- Interoperability
- Scalability
- Shared Security
Polkadot employs a relay chain which functions as the hub through which the parachains connect to and coordinates the consensus as well as transferring of messages and data between the parachains. Notably, both public and permissioned blockchains can connect to the network, with the ability of permissioned chains to isolate themselves from the rest of the system while still retaining the ability to transfer data to other chains and leverage the network’s security.
Parachains can be blockchains or other data structures that plug into the relay chain for pooled security and interoperability with other chains. However, they must meet the following criteria to be compatible with the Polkadot network:
- Can form compact and fast light client proofs
- Must be a method for a large number of independent authorities to authorize a transaction (i.e., Schnorr signature).
Parachains process their own transactions, which allows the network to scale based on concurrent independent processing of transactions per parachain which are secured via the broader network consensus.
The consensus of Polkadot is heavily inspired by Tendermint and HoneyBadgerBFT, but uses PoS as the primary method for incentivizing validators to be honest in the network.
Polkadot can also form ‘bridges’ with other chains that have their own consensus — such as Ethereum.
The bottom layers of the Polkadot protocol are known as the Polkadot Runtime Environment and are common throughout all the parachains on the network. These 3 layers consist of the Wasm interpreter, consensus, and networking.
The upper layers are unique to each connected parachain. Substrate — from Parity Technologies — is the first implementation of the Polkadot Runtime Environment (PRE). Parachains will be written using the PRE, which is built on the Web3 technology stack.
An important aspect of Polkadot is that it employs the Libp2p networking stack, and is the first real-world use of its Rust implementation.
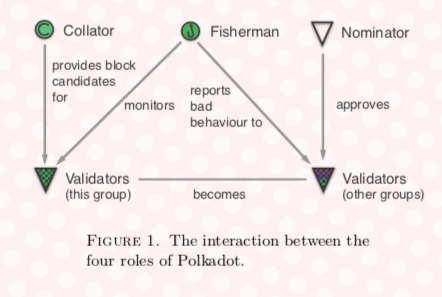
The dynamics of how Polkadot works are complex, so it is best to visualize the platform through the four primary participant roles in the ecosystem.
- Validators
- Nominators
- Collators
- Fishermen
Validators
Validators finalize the blocks in the Polkadot network and play the most critical role in the ecosystem. Validators are required to run the full relay chain client and need to stake a significant ‘bond’ (in the native DOT token) to qualify. However, validators can nominate other validators to act in their stead.
Validators receive candidate blocks from collators — who propagate selected blocks to validator subgroups from parachains — and finalize the blocks on the relay chain through a deterministic selection process and final round of validating ratification.
Nominators
Nominators are parties that also hold a stake in the network, but function as a mechanism for selecting trustworthy validators through contributing their bond to a select validator’s bond. Their role is very straightforward and helps strengthen the pooled security of the relay chain.
Collators
The collators work on the parachain level rather than directly with securing the relay chain. They gather transactions from the parachains, produce a proof along with an unsealed block, and send it to the appropriate validator charged with finalizing a parachain block. The Polkadot white paper notes that the role of collators may evolve, and eventually they may be contracted to work closely with specific validators for verifying blocks from certain parachains.
Collators can also work to prove malicious behavior to validators on the network as an added layer of security. The general role of collators is similar to the work of miners in PoW blockchains.
Fishermen
Fishermen are independent of the block verification process and seek out malicious behavior on the network that they report to validators about bad validators. They are motivated as ‘bounty-hunters’ looking for substantial one-off rewards by proving that a bonded party (i.e., validator or collator) acted maliciously outside of the rule set.
Fishermen post small bonds to the network too, however. This is to prevent Sybil attacks, but is not nearly as high as validators and can be withdrawn at any point.
Polkadot achieves a standardized communication across the network through its interchain communication protocol. Transactions between parachains or between parachain and relay chain are fully asynchronous, and all data transfers (even between parachains) are referenced on the relay chain.
Blockchains that are ‘bridged’ to Polkadot rather than directly plugged in as a parachain can leverage the standardized intercommunication of the network without sacrificing their own consensus. However, these chains forgo the shared state and security guarantees of the Polkadot network. Ethereum will be the first example of such a bridge on the platform.
DOT Token
Polkadot employs an on-chain governance model that is entirely controlled by the relay chain stakeholders. Stakeholders (i.e., validators) stake the native DOT token and can control everything from direct protocol upgrades to bug fixes.
Like other PoS consensus models, the native token is used for bonding and to incentivize validators to act honestly through having a financial stake in the authenticity of the verification process. Further, parachains connect to Polkadot through bonding and can be removed via withdrawing their stake from the network.
Polkadot is currently in its testnet POC-2 phase, where testDOT were used to upgrade the protocol from the POC-1 network and introduced several other features, including using the Rust implementation of Libp2p.
On-chain governance is a fascinating concept and is not only employed by Polkadot, but by other networks that are already live such as Tezos and Decred.
Applications of Polkadot
Since Polkadot does not make assumptions about the parachains connected to the network, it offers a wide range of flexibility for developers to build application-specific blockchains such as privacy-oriented ones or some focusing explicitly on certain dapp development.
Polkadot is also designed to facilitate faster innovation cycles. Features of one parachain can be leveraged on another, sharing innovation between chains and not simply just token transfers as the sole form of interoperability. Parachains are also free to focus on application building rather than having to focus on their own security. Parachains explicitly designed to function within Polkadot are part of the larger pooled security, creating a crucial abstraction of one of the more complicated components of blockchain networks for developers.
An intriguing example that Polkadot provides is the ability for users of a decentralized exchange on one parachain to deposit BTC onto the exchange using zero-knowledge proofs (ZKPs) by leveraging a ZCash parachain.
The potential applications of multi-chain frameworks are enormous and should help foster much more experimentation with new technologies born out of the sheer power of interoperability. However, consensus — particularly PoS — is complex and tricky to design around and has yet to be proven at a large scale in a decentralized network over considerable time, especially within a multi-chain environment.
Polkadot offers another promising glimpse into what the future generation of blockchains will look like, and may prove a gravitating setting for public and permissioned blockchains to come together and mutually benefit each other.
How to Buy Polkadot on Binance
After exploring where to buy and the coin’s use cases, the next thing is to explore how to buy it for your portfolio. Binance is our recommended exchange, so we'll explore how to purchase the asset using Binance.
Step 1: Sign Up
Go to the Binance home page and click on “Register”.
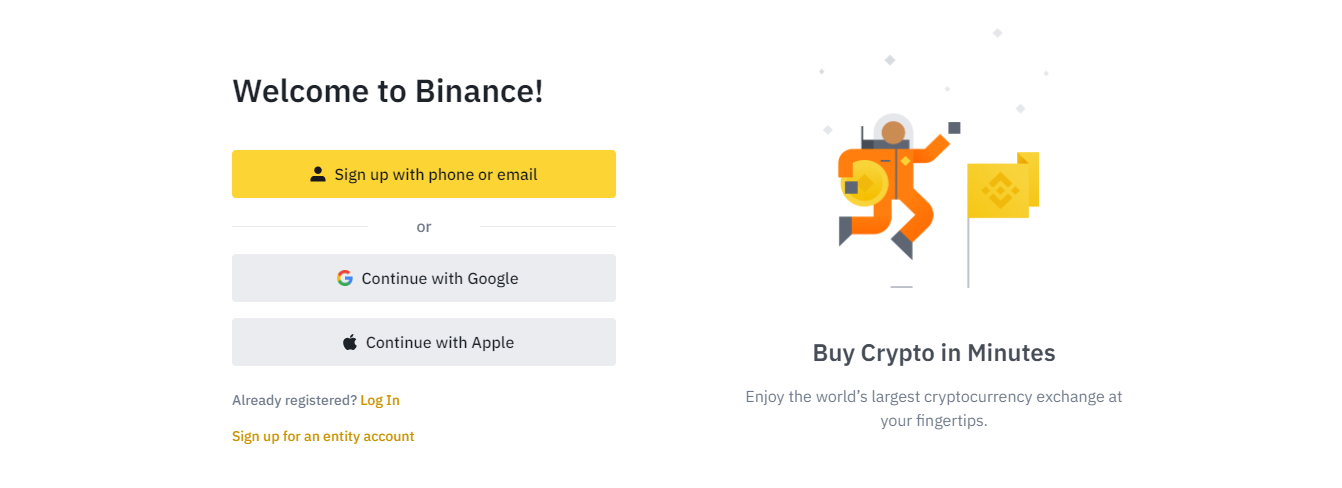
Binance allows investors to register using their mobile phone, email address, or Google account. Most users choose the first two options and provide their phone numbers, emails, and desired passwords. A link will be sent to their registration channel of choice, and investors can click on it to authenticate their accounts.
Step 2: Verify Your Identity
Like many other regulated brokers, Binance requires that investors verify their identity before commencing their purchase.
To complete the process, visit the “Identification” tab. Investors will have to share personal information, their proof of residence, and a government-verified means of identification. This process should take no more than a few minutes to complete.
Step 3: Deposit Your Funds
Next, investors will have to deposit into their Binance wallets. The exchange makes deposits possible using payment processors, wire transfers, bank deposits, and direct crypto transfers. And its required minimum deposit is $10.
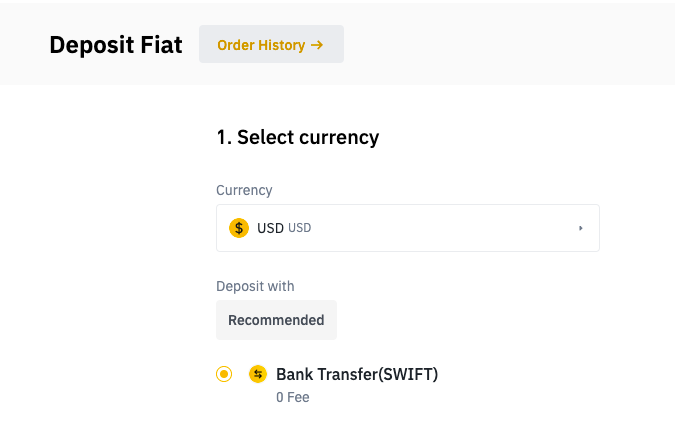
To make a deposit, go to the “Payment” section and click “Add a new payment method” to enter payment details. Alternatively, investors can click the “Buy Crypto” button to select a payment method and complete their transfer.
Step 4: Buy
With a funded wallet, investors are ready to make a your purchase. Head to the “Buy Crypto” section and enter the desired amount. Click on “Continue” after reviewing the terms, and the wallet should be updated immediately.
Polkadot Wallets
Software Wallet
Hot wallets, also called software wallets, are one of the most popular cryptocurrency storage options. They are always online, hence the affiliation with the ‘hot’ tag. Investors can easily get a hot wallet once they open an account with a crypto exchange. This allows them to store and manage their private keys, which prove their ownership of their assets to the blockchain network. Hot wallets are usually more convenient for everyday crypto transactions and can be custodial or non-custodial.

A custody wallet is responsible for storing assets to an exchange or a third-party platform. The user only places an order for a transfer or receipt, and the exchange signs off on the transaction, much like the traditional banking system. Meanwhile, a non-custodial or self-custody wallet gives the full responsibility to the end-user.
Hot wallets are usually free, but they are largely considered less secure due to their constant internet connectivity. An instance of a hot wallet is the Binance Wallet.
Hardware Wallet
A Hardware wallet is a device which has been created to provide an extra layer of security when interacting with your various cryptocurrency wallets.
Normally you would use your private key to move funds, the problem is though, if your computer has been compromised with malware or a virus, it is possible for your private keys to be captured and used to steal your funds.

With a hardware wallet, the private keys are stored on the device and never exposed to your computer, which means even if you are infected with such a program your private keys will remain safe. These options are safest way to store your crypto if you have more than a small amount.
Popular examples of cold storage offerings are the Ledger and Trezor line of hardware wallet solutions, read our reviews:
Mobile wallet
A mobile wallet is essentially a hot wallet on a smartphone device. They offer users an even more convenient way to use their coins for daily activities. Mobile wallets store and manage users' private keys while enabling them to pay for things they love with their digital assets.

These wallets are usually free and always online for transactions to be processed. Popular mobile wallets are eToro Money Wallet and Coinbase Wallet.
Desktop wallet
A desktop wallet is a PC version of a hot wallet. It is essentially software that an investor downloads into their personal computer or laptop for easy interaction with their digital coins. They also offer a browser extension which allows users to interact using an extension instead of downloading the entire software. Desktop wallets are also hack-prone due to their online nature. A popular example is the Exodus Wallet.
Paper Wallet
The paper wallet is arguably the oldest form of crypto wallet. They are no longer common in the modern crypto industry. It contains users' public and private keys. The paper wallet is the least secure type of wallet as it can easily be lost, stolen, or torched.





